Importing Excel spreadsheets
The Excel Spreadsheet Import ![]() action allows you to import data from an Excel worksheet or named range into a new or existing table, with more options available than for the Excel Multi-Sheet Import action. You can:
action allows you to import data from an Excel worksheet or named range into a new or existing table, with more options available than for the Excel Multi-Sheet Import action. You can:
- Select columns to import
- Select a subset of the data to be imported -
- Maximum number of rows
- Percentage of Rows
- When using an existing table as the output, use field mapping to map output fields to the existing table structure.
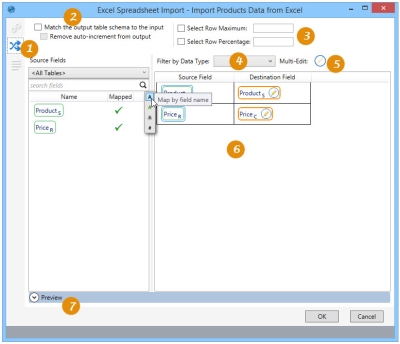
On the Mapping tab:
-
Define the mapping between input and output schemas.
-
Select the Match checkbox to map the output table schema to the input table.
-
Set limit on imported records.
-
Filter displayed mappings by data type.
-
Use the Multi-Edit option to edit properties of multiple selected fields simultaneously.
-
Review mapped fields.
-
Preview resulting filtered data or SQL statement.
The most common application is to import data stored in Excel spreadsheets.
Import Excel spreadsheet
- Drag the Excel Speadsheet Import icon onto the design surface.
-
On the Connections tab
 , enter a Name and a Description to identify the action, then specify the input Excel worksheet and output database table options:
, enter a Name and a Description to identify the action, then specify the input Excel worksheet and output database table options:Input -
- For Excel Connection, specify the Excel file from which the worksheet is being imported, or choose New Excel Connection to establish a new connection, and then choose the Worksheet that contains the data being imported.
Output -
- For Database Connection, specify the database to which the data is being imported, then enter or select a Table Name depending on the Output Mode you choose.
- For Create/overwrite a table, enter the name of the table. When you select this option -
- Optionally, add a new _autokey field to the table, with incremented values that make each table row unique.
- Indicate whether the output tables should be deleted following successful execution of the macro containing the import action.
Note that these options affect all output tables for this action.
- For Use an existing table, select the table from the drop-down. Note that you may be required to map data columns if the input and output schemas are different. When you select this option -
- Indicate whether the table should be cleared after the macro or workflow has executed.
- For Create/overwrite a table, enter the name of the table. When you select this option -
- You can also create an output table containing those records that do not import successfully. To do this, select the Failure Table Name checkbox, and either enter a name for the table or accept the default name, which is based on the name of the output table and appended with _Failures. Failed records, if encountered, are written to the table as is, and must be resolved manually.
- On the Mapping tab
 , indicate how the data is mapped between the Excel spreadsheet and output database table. Refer to Field Mapping for more information.
, indicate how the data is mapped between the Excel spreadsheet and output database table. Refer to Field Mapping for more information. - If enabled in User Preferences, use the Performance tab
 to change certain execution settings specific to the action. Refer to Change general preferences for additional information.
to change certain execution settings specific to the action. Refer to Change general preferences for additional information.
Last modified: Thursday December 19, 2024