OrderBy function
The OrderBy function defines the logical order of the rows within a query's results. It supports multiple parameters, so you can order data by multiple fields with one instance of OrderBy. If you use multiple parameters, the results are ordered by the first parameter, then the second, and so on. This function is available wherever the Statement Editor is used, including in app boards and dynamic views.
Ascending order is used by default, but the DESC option can be used to specify a descending order. In the Statement Editor interface, select the Desc icon  to switch to descending order. In the Statement Text Editor, add DESC to the function.
to switch to descending order. In the Statement Text Editor, add DESC to the function.
Some functions such as Rank, DenseRank, and RowNumber require the OrderBy function. See a function's topic to see if it requires the OrderBy function.
The syntax of the function is:
<table>.<field>.<function>.OrderBy(<field1>, <field2>, ...DESC).
where DESC is optional and <fieldX> could be:
- <table>.<field>
- the result of another function such as If. For example, you could partition by the Pareto category provided by an If function.
OrderBy can be use with PartitionBy to order each partition. If used with the PartitionBy function, OrderBy is applied to each partition separately and computation restarts for each partition. If the functions are used together, OrderBy must appear after PartitionBy:
<table>.<field>.<function>.PartitionBy(<table>.<field>).OrderBy(<table>.<field>)
The OrderBy function can be used to help create a running cumulative percent of an entire table or a running percent of total (Pareto analysis).
Use cases
Using with OrderBy
The Order By function can be used to order results without partitioning. The following example accumulates orders by quantity, and orders them by quantity in descending order.
Orders.quantity.Sum().OrderBy(Orders.quantity DESC)
This would give the following result from a sample Orders table:
| Product | Location | Quantity | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| f | 3 | 6 | 6 |
| e | 3 | 5 | 11 |
| d | 2 | 4 | 15 |
| c | 2 | 3 | 18 |
| b | 1 | 2 | 20 |
| a | 1 | 1 | 21 |
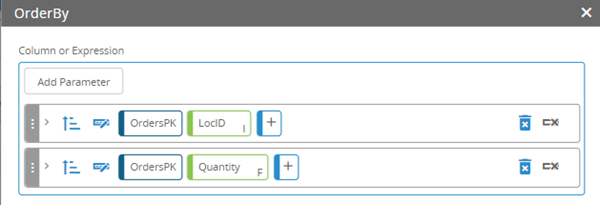
Ordering with two parameters
In the following example, the Order By function is being used to order the data by location ID and quantity. Note the ability to sort using the ascending  or descending
or descending  icons on the parameter lines.
icons on the parameter lines.
Using with PartitionBy
The Order By function can be used with the Partition By function to partition, accumulate, and order results by a field. If these functions are used together, Order By must appear after Partition By in the statement. The Order By function is then applied to each partition separately and computation restarts for each partition.
The following example partitions and accumulates orders by location, and orders them by quantity:
Orders.quantity.Sum().PartitionBy(Orders.location).OrderBy(Orders.quantity)
This would give the following result from a sample Orders table:
| Product | Location | Quantity | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| b | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| c | 2 | 3 | 3 |
| d | 2 | 4 | 7 |
| e | 3 | 5 | 5 |
| f | 3 | 6 | 11 |
Last modified: Friday May 12, 2023
