Life cycle algorithms
In Demand Guru, life cycle models and the algorithms that support them fall into two categories:
- Non-linear models are generally comprised of five stages that include Launch, Growth, Maturity, Decline Obsolescence.
- Piecewise-linear models are generally comprised of fewer stages that each encompass more of the total life cycle.
In addition, a tournament of all these models can be used to provide the best modeling option. See Effect of algorithms on life cycle curve for detailed descriptions of these models, including the three major parameters which are used to characterize these models.
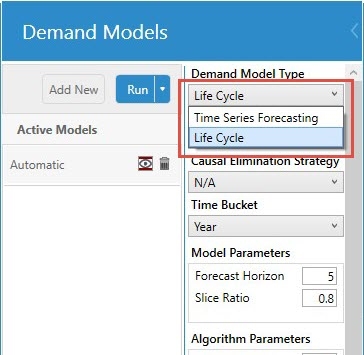
Use the Demand Models section of the Demand Modeling tab in the workbench to choose a life cycle algorithm and begin modeling.
- For Demand Model Type, use the drop-down to select Life Cycle.
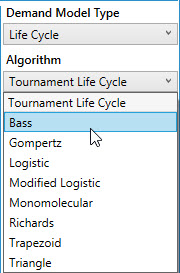
- For Algorithm, use the drop-down to select a modeling algorithm. Available choices include all individual algorithms supported for life cycle modeling, plus the Tournament Life Cycle choice which allows you to run all the non-linear algorithms in a tournament mode.
Once you select an algorithm, the Algorithm Parameters section is populated with the parameters available for that algorithm. In addition to the Adjust Outliers parameter used by all algorithms, each life cycle algorithm supports several additional custom parameters.
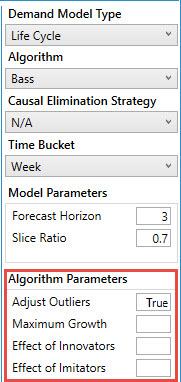
- Enter values for the parameters to be used.
- As shown, Bass supports Maximum Growth, Effect of Innovators, and Effect of Imitators.
- Logistic, Richards, and Gompertz support Maximum Growth, Slope, and Lag Phase.
- Modified Logistic and Monomolecular both support Initial Value and Maximum Growth; however, Modified Logistic Model supports Lag Phase, while Monomolecular supports Slope.
- Tournament Life Cycle supports Maximum Growth (except when running Trapezoid or Triangle), Model Selection Criteria, and Model Names.
The Model Names parameter identifies the underlying models that will be run during execution of Tournament Life Cycle. The default for this entry is to run all available non-linear algorithms (Logistic, Modified Logistic, Richards, Gompertz, Bass, and Monomolecular); however, you can choose any combination of models.
- Trapezoid and Triangle support Product Life, Half Life, Growth Slope, and Decline Slope; Trapezoid also supports Declination Point.
Last modified: Thursday December 19, 2024