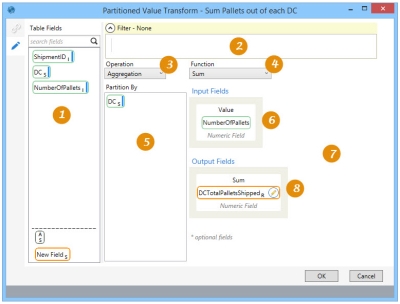
Partitioning data records based on calculations
The Partitioned Value ![]() action allows you to perform calculations such as aggregations, ranks, and running totals from a “vertical” perspective, progressing down a column. The table can be partitioned to perform these calculations separately on each subset of the table rows. You can:
action allows you to perform calculations such as aggregations, ranks, and running totals from a “vertical” perspective, progressing down a column. The table can be partitioned to perform these calculations separately on each subset of the table rows. You can:
- Choose the operation and function to perform on the input field(s).
- Partition by fields to define the subsets of the target table for which the operation is applied.
- Define the output fields to be returned as additional columns in the target table.
On the Configuration tab:
-
Use the Table Fields to defined filters, partitioning, and input/output fields.
-
Define a filter to limit partitioned records.
-
Select the operation by which to partition the values.
-
Select the function to be used when determining ranking by row.
-
Define the fields by which to partition the values.
-
Define the fields to be used as input.
-
Define the field(s) used to determine the sort order of the input field(s) (for Rank or Running Total, not shown); use arrows to set ascending or descending order.
-
Specify the output field(s).
Possible applications include:
- Rank records based on a column value
- Calculate the running total or running percentage of total of a column value
- Calculate the percentage of sum, sum, count, minimum, or maximum of values in a column
Partition records by value
- Drag the Partitioned Value icon onto the design surface.
-
On the Connections tab
 , enter a Name and a Description to identify the action, then specify the target database and table.
, enter a Name and a Description to identify the action, then specify the target database and table.- For Database Connection, select the database in which the values are being partitioned, or choose New Database Connection to establish a new connection.
- For Table Name, select the table in which to partition the values.
- On the Configuration tab
 :
: - Select an Operation and Function to be performed -
Operation Function Description Aggregation Percent of Sum Calculates Quantity as percentage of partition’s sum. Aggregation
Sum Calculate sum of Quantity field for each partition and save result in Output field of each row. Aggregation Count Count number of fields in each partition and save result in Output field of each row. Aggregation Min Determine minimum value of Quantity field for each partition and save result in Output field of each row. Aggregation Max Determine maximum value of Quantity field for each partition and save result in Output field of each row. Rank Ordinal Rank rows by evaluating Quantity field in either ascending or descending order. Each row has unique rank, even if two or more rows have equal values for Quantity field. Rank Competition Rank rows by evaluating Quantity field in either ascending or descending order. Rows with equal values for Quantity field are ranked with equal values, and ties cause rank values to be skipped. For example, possible rank values can be 1, 2, 2, 4, 4, 4, 4, 8, 9, 10 Rank Dense Ranks rows by evaluating Quantity field in either ascending or descending order. Rows with equal values for Quantity field are ranked with equal values, and ties DO NOT cause rank values to be skipped. For example, possible rank values can be 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4, 5, 6 Running Total Running Total Conceptually, includes 2 phases: first phase ranks rows in each partition (similar to Rank–Ordinal), second phase calculates running total for each row based on ranking and stores value in Output field. Running Total Running Percent of Total Similar to Running Total function; however, Output field is populated with running total proportional to total of all Quantity values in partition. - Drag the icon for a field by which data is being partitioned from Table Fields into Partition By.
- Drag the icon for a field serving as the quantity to Input Fields. Note that the field you are adding must be numeric.
- If using Rank or Running Total, select up to two Order By Fields for the input field, and use the arrows next to the field(s) to indicate ascending or descending order.
- Drag the icon for a field (or fields if using the Running Total operation) from Table Fields to Output Fields.
- Use the Filter area to build an expression that more narrowly defines the data to be partitioned. Expressions can be created directly in the Filter area, or you can use the Expression Editor.
- Select an Operation and Function to be performed -
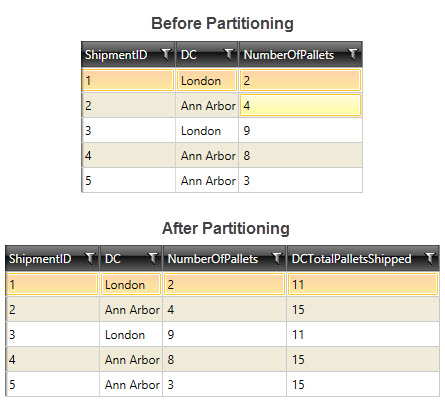
Partitioned Value data example
Last modified: Thursday December 19, 2024