Import data
The import data feature allows you to import data from .txt, .csv, .xls, .xlsx, .mdb, and .accdb format files. You can select which sheets or tables are included in the import and you can select the specific columns to import from the source. Additionally, you can map the column from the source that is associated with the target column.
If you are importing from Microsoft Access databases, or using them as data sources for input pipes, you may need to install the Microsoft Access Database Engine Redistributable.
- Microsoft Office 2016 – If you have the 2016 version of Microsoft Office installed, download and install the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2016 Redistributable:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54920
- Microsoft Office prior to 2016 – If you have a version of Microsoft Office installed that is earlier than the 2016 version, download and install the Microsoft Access Database Engine 2010 Redistributable:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=13255
- Select Model > Import Data.
- Click Add and select a valid import file (one of .txt, .csv, .xls, .xlsx, .mdb, and .accdb). You can continue to add data sources to the list. Supply Chain Guru X will attempt to map input from the data source to model tables. Those that have been successfully mapped and are valid for import are displayed with green checkmarks
 and selected for import by default. If you are importing one of .txt, .csv, .xls, and .xlsx, there is a record limit of 1,048,576. For Excel files, this limit is per worksheet within the file.You can hover over the filename of data source to display the full path in a tooltip.
and selected for import by default. If you are importing one of .txt, .csv, .xls, and .xlsx, there is a record limit of 1,048,576. For Excel files, this limit is per worksheet within the file.You can hover over the filename of data source to display the full path in a tooltip. - The first table in the data source is displayed with the mapping form for the selected table/sheet. You can click on other tables in the data source tables to display the mapping form for that table.
- If required, select the Target Table from the drop-down list.
- Check or uncheck individual columns to import. Required fields are identified in bold at the top of the Target Column drop-down list. These fields must be mapped for the import to be valid. If required fields are not yet mapped, they will be listed immediately below the Field Mapping section.
- To map a Source Column to a column in the Target Table, select the Target Column from the drop-down list.
- Select one of the following actions for each table:
- Replace – Replaces all data in the target table by deleting existing rows before import. Replace is the default action.
- Append – Appends rows from the Excel file to those already in the target table.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 for additional tables requiring a mapping configuration.
- Check or uncheck individual tables as required for the import.
If a table or sheet name is displayed with a red X
 , this indicates that required fields are not currently mapped for import:
, this indicates that required fields are not currently mapped for import: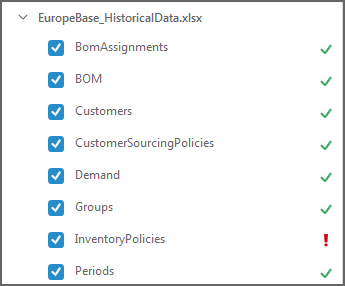
- Click Import. The data is imported.
If there are errors detected, these are displayed on the Import Data Errors form. You can do one of:
- Cancel – Cancels the import operation.
- Retry Import – Retries the current import operation.
- Ignore Errors – Attempts to import the data even if errors are reported. Supply Chain Guru X will discard any rows that contain errors.
- Select a row and click Open Data Source – The import file is opened using the program that is associated with the file type.
For columns that support a Unit Of Measure, if the imported value does not include the Unit Of Measure Symbol, the default Unit Of Measure as defined in Model > Model Settings > Units and Currency is assumed.
Import data formats
When importing data using the Import Data function in the Model menu, you can use files in one of several supported formats:
- Microsoft Excel (.xlsx, .xls)
- Comma separated value (.csv)
- Tab delimited text (.txt)
- Microsoft Access (.accdb, .mdb)
Keep the following in mind to ensure successful imports:
- Excel, csv and txt files should include a row with column headers. In Access, the names of the table columns will be the used.
- You do not need to populate all columns in the target table, although you must populate the required columns such as Name in the Products table. Any missing columns will be skipped.
- Column names do not need to match those in the Supply Chain Guru X model database. If column names do not match, you have the opportunity to map columns from the source to the destination.
- For the comma separated value format (.csv), if any of your field values contain a comma, you must enclose the entire value in quotes. For example, "Retail pack, 24 piece" ensures that the value is not separated into 2 different columns.
Excel format
You can easily create a template Excel file by exporting from a data table or using the Export Data function in the Model menu to export a number of tables. When using Export Data, you have an option to "Export only structure".
If you are creating the Excel file outside Supply Chain Guru X, create a separate sheet for each Supply Chain Guru X you want to import into. The sheet name should reflect the target table in Supply Chain Guru X. In the first row of each sheet enter the column names. Each data row should be populated with values in the order of the column headings
Comma separated value format
In this format, create a row with the column headings, separated by commas. Each data row should be populated with values in the order of the column headings, separated by commas. The following is an example of a .csv file that can be used to populate records in the Products table. Note that we have enclosed the Name value in the third record in quotes, since it includes a comma. For columns not included in the source file, if default values are defined, these values are populated in the new records.
Name,Unit Price,Unit Weight,Unit Volume,Type,Class,Status
Raw Material_01,0,10,1,Discrete,100,Include
Raw Material_02,0,10,1,Discrete,100,Include
"Raw, Alternative Material_03",0,10,1,Discrete,100,Include
Tab delimited text format
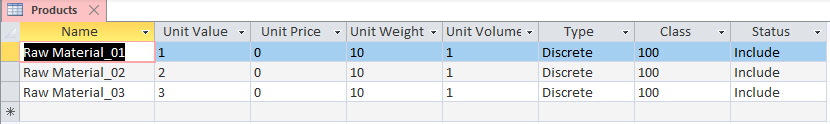
In this format, create a row with the column headings, separated by tabs. Each data row should be populated with values in the order of the column headings, separated by tabs. The following is an example of a .txt file that can be used to populate records in the Products table. For columns not included in the source file, if default values are defined, these values are populated in the new records.
| Name | Unit Value | Unit Price | Unit Weight | Type | Class | Status | ||
| Raw Material_01 | 1 | 0 | 10 | Discrete | 100 | Include | ||
| Raw Material_02 | 2 | 0 | 10 | Discrete | 100 | Include | ||
| Raw Material_03 | 3 | 0 | 10 | Discrete | 100 | Include | ||
Access format
In Access, create a separate table for each Supply Chain Guru X you want to import into. Define the Field Name values in Access as the column names, then enter records with values populated in the order of the columns.
Last modified: Wednesday May 15, 2024
