Formula propagation
The formula propagation method uses the statistically acceptable formula.
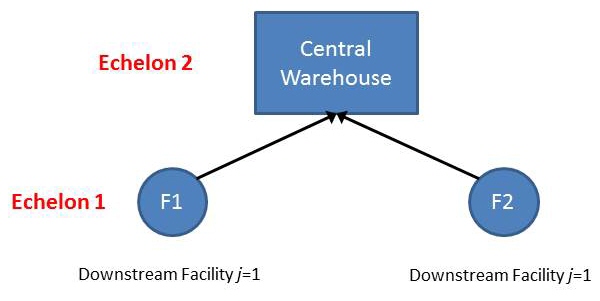
Demand Analysis performs the following steps during formula-based demand propagation:
Step 1: Estimate the ordering process parameters for downstream facilities.
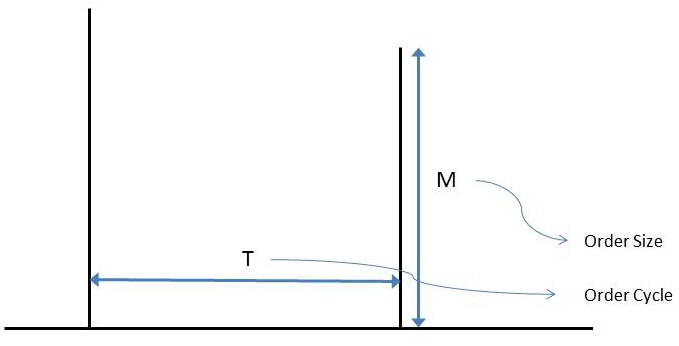
Moments of order size (M) under large minimum order quantity assumption:
Average replenishment qty = E[M] = q and
Second raw moment of replenishment qty = E[M2 ] = q2
where q is the minimum order quantity.
Moments of order size (M) under small minimum order quantity assumption:
Average replenishment qty = 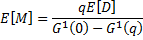
Second raw moment of replenishment qty = E[M2 ] = numerical procedure
Moments of R: (# of customers arriving during an order cycle):
(Average) 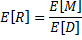
(Second raw moment) 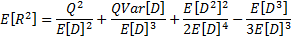
Moments of order cycle:
(Average) E[T] = E[R].E[A]
(Second raw moment) E[T2 ] = E[R].Var[A] + E[R2 ].E[A]2
Step 2: Estimate the demand process parameters for upstream facilities.
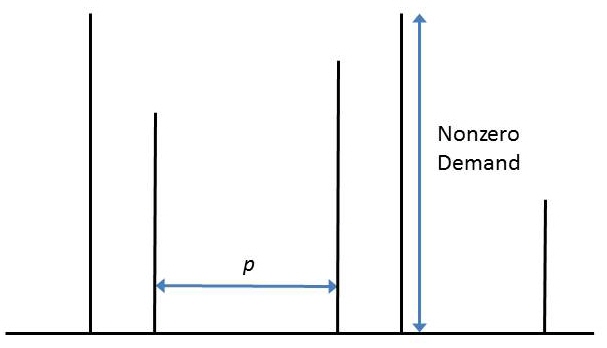
Inter-demand interval mean:
(mean) 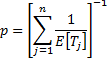 for each downstream site j
for each downstream site j
Moments of demand size (non-zero demand):
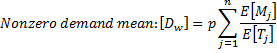 for each downstream site j
for each downstream site j
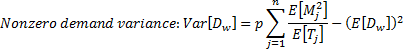
for each downstream site j
Step 3: Estimate the demand mean (μ) and the variance (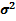 ).
).
Demand mean:
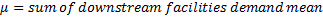
Demand variance:
Case1: Unit batch size: q=1:
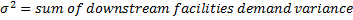
Case2: Non-unit batch size: q>1:
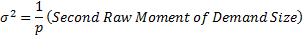
where
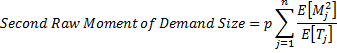
for each downstream site j
One case in which you may want to use "Formula" as the propagation method is when you do not have demand data but you know what the mean and standard deviation values are. This is often the case when working with forecast data. You may not have daily or weekly demand numbers, but instead you have one average number. In this case, you can enter this information in the User Defined Site Forecast Profile to be used as an input, and select "Formula" as the propagation method for Demand Analysis.
Last modified: Wednesday May 15, 2024
