Intermittent demand forecasting
An intermittent demand series refers to a time series that includes a significant amount of zero values. When a demand series is decomposed into non-zero demand and inter-demand interval time series, it can be identified as an intermittent demand series.
An inter-demand interval time series is used to identify intermittency. If the estimated mean is greater than or equal to 1.32, the demand series is classified as intermittent.
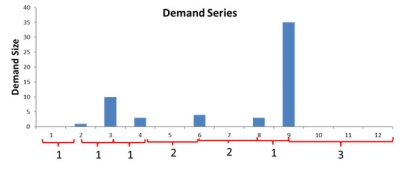
For example, consider the following demand series:
This example shows an inter-demand interval time series of {1,1,1,2,3,1,3}. If ρ is an estimate for the inter-demand interval mean, the calculation is as follows:
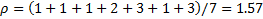
Intermittent demand must be forecasted differently than a typical demand series. The classical method predicts the average demand amount per time period rather than the next demand series value.
Croston (1972) developed the first intermittent forecast method, and all other work resembling his method is referred to as Croston-type Intermittent Demand Forecasting. In the Croston method, two separate exponential smoothing methods are used to predict demand size and inter-demand intervals. The average demand value (prediction) is estimated as a ratio of demand size estimate over inter-demand interval estimate. The average demand values are updated only in the periods with positive demand.
Coupa uses three different Croston-type intermittent demand forecasting methods:
- Croston
- SBA (Syntetos Boylan Approximation)
- SBJ (Shale-Boylan-Johnston)
In addition, an automatic selection algorithm (Auto) is available which uses a classification method to select automatically between Croston, SBA, and simple exponential smoothing (SES) to provide the best modeling option.
The following notation is used to characterize the forecasting models.
-
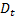 - demand in period t
- demand in period t -
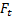 - forecast of demand per period made in period t for period t+1
- forecast of demand per period made in period t for period t+1 -
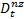 - non-zero demand in period t when demand occurs with mean
- non-zero demand in period t when demand occurs with mean 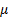 and variance
and variance 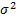
-
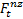 -forecast of non-zero demand in period t
-forecast of non-zero demand in period t -
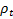 - inter-demand interval in period t
- inter-demand interval in period t -
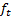 - estimate (i.e. forecast) for inter-demand interval in period t
- estimate (i.e. forecast) for inter-demand interval in period t -
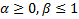 - smoothing parameters
- smoothing parameters
Last modified: Thursday December 19, 2024