Cleanse a product master table
When receiving a new data set, cleansing the data to transform it into a standard, consumable format is an important first step. A new data set may have issues such as blank and null values, leading or trailing spaces, and undesired characters. These issues can wreak havoc on downstream data blending and analysis processes. Data Guru actions can be used to explore a data set to identify such issues and then correct those issues.
This example includes the following actions to assess data quality issues, correct those issues, and extract desired information from strings of text:
- Data Profiling
- Adjustment
- Text Parsing
The data in this example is made available using an Excel file connection named DG: Product Master. The worksheet is imported into a new table called Product_Master, which contains a sample list of products with the following information:
- Product code/SKU (field name ProductCode)
- Product description, which contains the units per case and weight per unit within the long string of text (field name ProductDescription)
- Product line (field name ProductLine)
Once the table is imported, you can cleanse the data.
Step 1 - Rather than looking at the standard table output, use Data Profiling to understand the new data source and the data quality issues it contains.
- Specify the Product_Master as the input table, and ProductMasterImport as the Base Table Name.
- On the Configuration tab, click >> to select all the fields.
- Upon completion of the action, open the ProductMasterImport_TS file to view the profiling.
Step 2 - Use the Alter Data Type transform to adjust the data type of the ProductCode field from integer to string.
It is not necessary to store the Product Code as an integer, because you do not have to perform calculations or numerical analysis on the field. Storing the ProductCode as a String allows you to pad the beginning of each record with zeros to standardize the length of the product code.
- Specify the Product_Master as the target table.
- On the Configuration tab, alter the ProductCode to be of Data Type StringU (255).
Step 3 - Use the Adjustment action to cleanse the ProductCode and ProductLine fields.
The ProductCode field should be cleansed to include leading zeros that create 10-character codes. The ProductLine field should have symbols and leading and trailing spaces removed.
- Specify the Product_Master as the target table.
- On the Configuration tab, alter the ProductCode to be of Data Type StringU (255).
- In the first Functions card, use the Pad Left function to add zeros to the beginning of every ProductCode that contains less than 10 characters, until the code contains ten characters.
- On the next card, use the Removed Characters function to remove all characters that are not letters from each line in the ProductLine field.
- On the last card, use the Trim Full function to removing leading and trailing spaces from every record in the ProductLine field.

Step 4 - Use the Text Parsing action to cleanse the ProductDescription column and create new columns to store the units per case and the weight per unit information.
In the ProductDescription column, notice the two numbers contained within the strings of text. They represent the number of units per case and the weight per unit of each product. We need these numbers extracted from the ProductDescription column. To do this, we can identify a pattern in the ProductDescription column and apply a regular expression in the Text Parsing transform.
- Specify the Product_Master as the target table.
- On the Configuration tab, specify the ProductDescription as the input string.
- Apply the expression shown here and assign the first substring to a new UnitsPerCase column. Assign the second substring to the WeightPerUnit column.
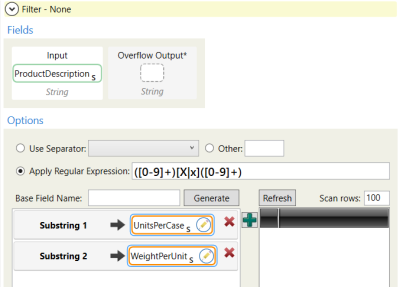
Some records in the ProductDescription column had a different pattern, and no values were extracted. To fill in these values, you can take the averages of similar products and use the averages for the records that were blank.
Step 5 - Use the Change Data Type action to change the data types of the new columns to a numeric type that can be averaged.
- Specify Product_Master as the target.
- On the Configuration tab, make UnitsPerCase and WeightPerUnit the columns to alter.
- For both columns, select Double as the Data Type.
Step 6 - Use the Aggregation action to calculate the average units per case and average weight per unit of each product line, and apply the average to the missing values based on the Product Line.
- Specify Product_Master as the input table and a new ProductLine_AverageCaseSize table as the output table.
- On the Configuration tab, use the AVG function over the UnitsPerCase field to create the AVGOfUnitsPerCase value.
- On the Configuration tab, use the AVG function over the WeightPerUnit field to create the AVGOfWeightPerUnit value.
- On the Mapping tab, map the ProductLine, AVGOfUnitsPerCase, and AVGOfWeightPerUnit values to the ProductLine, AVGOfUnitsPerCase, and AVGOfWeightPerUnit columns in the ProductLine_AverageCaseSize table.
Step 7 - Use the Update action to copy the average values from the ProductLine_AverageCaseSize table to the Product_Master table.
- Specify Product_Master as the target table and a new ProductLine_AverageCaseSize table as the lookup table.
- On the Configuration tab, use the IsNullAll function to specify only the records with no value in the UnitsPerCase and WeightPerUnit columns.
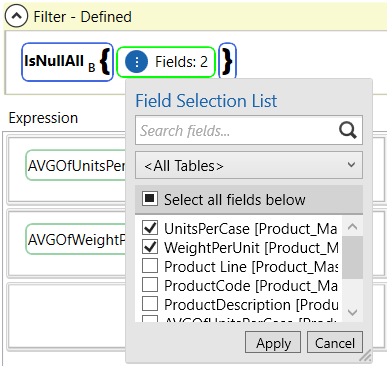
- Specify an expression to copy the AVGOfUnitsPerCase value to the UnitsPerCase column and the AVGOfWeightPerUnit value to the WeightPerUnit column.
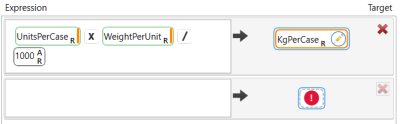
Step 8 - Use the Update action to calculate the weight per case for each product.
- Specify Product_Master as the target. A lookup table is not necessary.
- On the Configuration tab, specify an expression to create a KgPerCase field, which is generated by multiplying UnitsPerCase by WeightPerUnit and dividing by 1000 (from grams to kilograms).
Last modified: Thursday December 19, 2024
